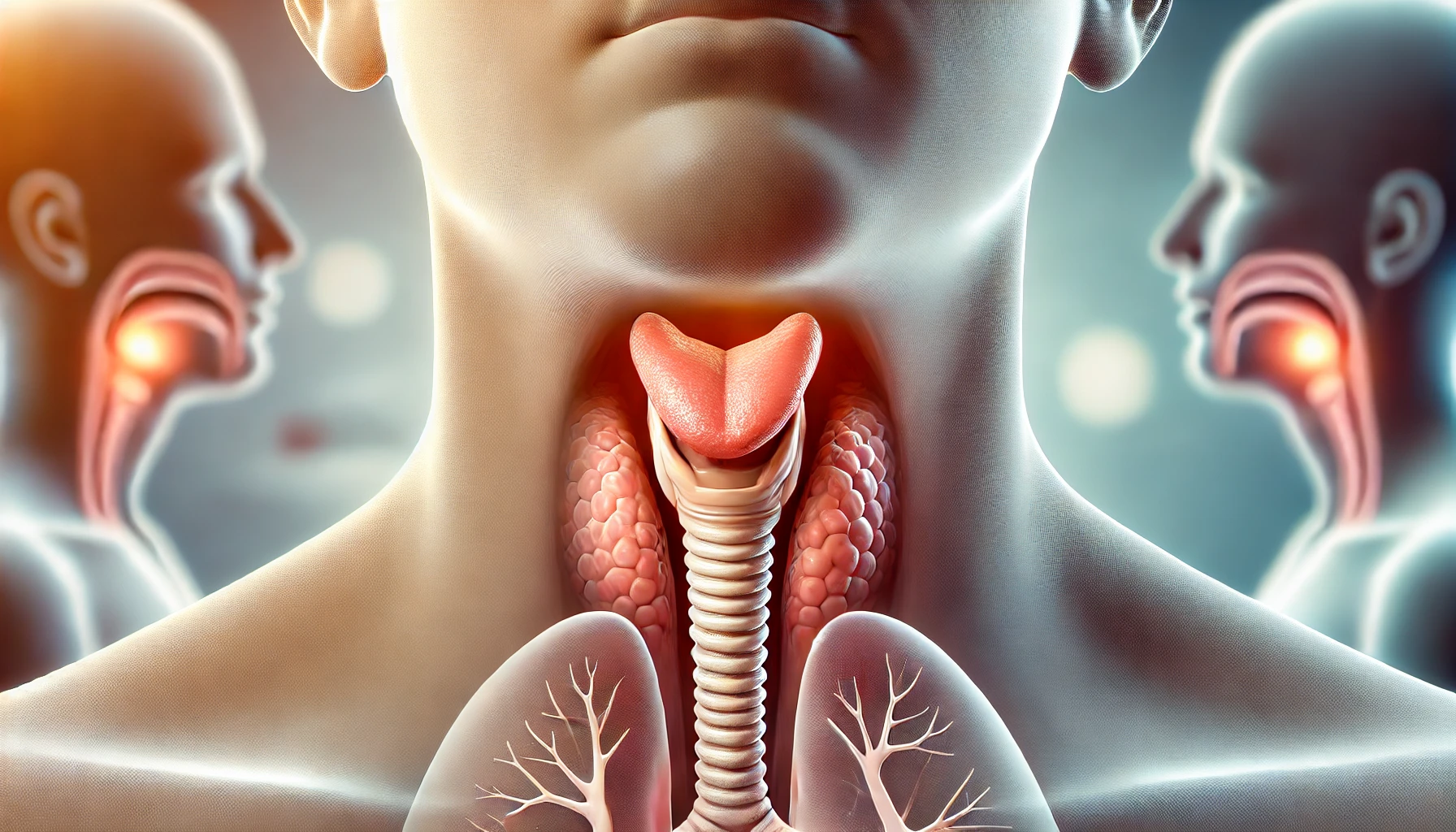
The human uvula (Biyomon Uvula) is a small, fleshy extension located at the back of the throat, hanging down from the soft palate. It plays an important role in speech and swallowing, helping to prevent food from entering the nasal passages during eating. While the uvula is usually unnoticed by most people, issues with the uvula can cause discomfort, irritation, or even more serious medical conditions.
In this article, we will explore the various conditions that can affect the uvula, including uvulitis, uvular swelling (Biyomon Uvula), and elongation. We’ll also discuss potential causes, symptoms, and treatments for these issues, focusing particularly on understanding the condition referred to as “Biyomon Uvula”—a term that may be unfamiliar to many, but which highlights a specific set of uvula-related problems.
We’ll also touch upon how to maintain proper uvula health, what happens if uvula-related issues go untreated, and the available medical treatments. At the end of this guide, we will address frequently asked questions (FAQs) to provide further insights into uvula health and care.
What is the Uvula?
The uvula is a small, conical-shaped organ located at the back of the mouth, hanging from the soft palate. It is composed of connective tissue, muscle fibers, and glands, and serves several important functions in both speech and swallowing – Biyomon Uvula.
Key Functions of the Uvula
- Speech Articulation: The uvula helps in producing certain sounds, particularly guttural sounds, such as those found in languages like French and Arabic. It is involved in the articulation of certain consonants by vibrating as air passes over it.
- Swallowing and Preventing Nasal Regurgitation: When you swallow, the uvula works with the soft palate to close off the nasal passages, preventing food or liquids from entering the nasal cavity. This helps ensure that food moves smoothly down the throat and into the esophagus.
- Moistening the Throat: The uvula contains glands that secrete saliva, which helps keep the throat moist and lubricated. This is important for comfortable speech and swallowing.
- Immune Function: The uvula is part of the body’s immune system, acting as a barrier against pathogens that might enter through the mouth. It contributes to the mucous membrane system, which captures and expels bacteria and viruses.
Common Uvula Problems and Conditions
While the uvula (Biyomon Uvula) usually goes unnoticed, there are several conditions that can affect it and cause discomfort or even medical complications. These conditions may require medical attention or even surgical intervention if they worsen or persist. Here are some common issues that can affect the uvula:
1. Uvulitis
Uvulitis refers to the inflammation and swelling of the uvula (Biyomon Uvula). This condition can cause the uvula to become red, swollen, and painful. In severe cases, the uvula may become so swollen that it obstructs the airway, making it difficult to breathe.
Causes of Uvulitis
Uvulitis can be caused by a variety of factors, including:
- Infections: Viral or bacterial infections such as strep throat, tonsillitis, or the common cold can cause uvulitis.
- Allergic Reactions: Allergies to certain foods, medications, or environmental factors can trigger an immune response that causes the uvula to swell.
- Dehydration: When the body is dehydrated, the tissues in the throat, including the uvula, may swell due to lack of moisture.
- Trauma: Physical trauma, such as accidentally biting the uvula or irritation from dental procedures, can lead to swelling and inflammation.
Symptoms of Uvulitis
The most common symptoms of uvulitis (Biyomon Uvula) include:
- Swollen and red uvula
- Sore throat
- Difficulty swallowing
- Gagging or choking sensation
- Snoring due to partial airway obstruction
- In severe cases, difficulty breathing
Treatment of Uvulitis
Treatment for uvulitis depends on the underlying cause – Biyomon Uvula:
- Antibiotics or Antivirals: If a bacterial or viral infection is the cause, medications will be prescribed to treat the infection.
- Allergy Management: If an allergic reaction is the culprit, antihistamines or corticosteroids may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and swelling.
- Hydration: Drinking plenty of fluids can help keep the uvula and throat tissues moist, reducing swelling caused by dehydration.
- Pain Relief: Over-the-counter pain relievers such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can help alleviate discomfort associated with uvulitis.
2. Uvular Swelling (Uvular Edema)
Uvular swelling, or uvular edema, occurs when the uvula becomes engorged with fluid, causing it to expand in size. This condition can be alarming, especially if the swollen uvula comes into contact with the tongue, creating a sensation of choking.
Causes of Uvular Swelling
Uvular swelling can be caused by – Biyomon Uvula:
- Sleep Apnea: Repeated snoring and airway obstruction in people with sleep apnea can lead to uvular swelling.
- Dehydration: Just like uvulitis, dehydration can cause the tissues of the uvula to swell.
- Infections: Respiratory infections, such as colds and flu, can cause uvular swelling as part of the body’s immune response.
- Chemical Irritants: Inhalation of smoke, chemicals, or pollutants can irritate the uvula and cause it to swell.
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease (GERD): Acid reflux from the stomach can irritate the uvula and cause it to swell over time.
Symptoms of Uvular Swelling
- Noticeable enlargement of the uvula
- Sensation of something stuck in the throat
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Snoring or sleep disruptions
Treatment for Uvular Swelling
- Hydration: Drinking water and using throat sprays or lozenges can help reduce swelling.
- Treating Underlying Conditions: Managing sleep apnea, GERD, or infections can prevent future occurrences of uvular swelling.
- Steroids: In severe cases, doctors may prescribe corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
3. Elongated Uvula (Uvuloptosis)
An elongated uvula (Biyomon Uvula) is a condition in which the uvula becomes abnormally long, often causing discomfort, snoring, and a sensation of a foreign object in the throat. While an elongated uvula is not necessarily harmful, it can contribute to sleep-related breathing disorders such as sleep apnea.
Causes of an Elongated Uvula
The causes of an elongated uvula (Biyomon Uvula) include:
- Genetics: Some individuals are born with a naturally longer uvula.
- Chronic Irritation: Smoking, exposure to environmental irritants, or frequent snoring can cause the uvula to elongate over time.
- Obstructive Sleep Apnea: Sleep apnea and other sleep disorders can result in repetitive stress on the uvula, causing it to elongate.
Symptoms of an Elongated Uvula
- Feeling of something stuck in the throat
- Gagging or choking sensations
- Persistent snoring
- Difficulty swallowing
- Chronic cough
Treatment for an Elongated Uvula
- Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP): A surgical procedure to remove part of the uvula and soft palate to prevent airway obstruction and reduce snoring or sleep apnea symptoms.
- Lifestyle Changes: Quitting smoking and reducing exposure to environmental irritants can help prevent further elongation of the uvula – Biyomon Uvula.
4. Uvula Deviation
A deviated uvula occurs when the uvula is not centered but instead veers to one side of the mouth. While this condition is often harmless, it can be a sign of an underlying neurological or muscular issue – Biyomon Uvula.
Causes of Uvula Deviation
- Tonsillectomy or Surgery: The uvula may become deviated after certain surgeries, such as tonsillectomies, due to scarring or tissue manipulation.
- Neurological Conditions: Conditions such as stroke or cranial nerve palsy can cause the muscles in the soft palate to weaken, leading to uvula deviation.
- Trauma or Infection: Trauma to the throat or severe infections can lead to uvula deviation.
Symptoms of Uvula Deviation
- Uvula visibly off-center
- Difficulty swallowing or speaking clearly
- Sleep disturbances or snoring
- Possible symptoms of underlying neurological conditions, such as facial drooping
Treatment for Uvula Deviation
- Medical Examination: A thorough examination is necessary to determine if the uvula deviation is due to a neurological condition or structural issue.
- Treatment for Underlying Conditions: If the deviation is caused by an infection or trauma, treating the underlying issue will help resolve the deviation.
- Surgery: In severe cases, surgical correction may be necessary to restore the uvula’s proper position.
What is “Biyomon Uvula”?
“Biyomon Uvula” is a term that seems to have emerged from a fusion of medical terminology and cultural or fictional references. The term “Biyomon” may relate to a name or character from pop culture, such as the Digimon universe, but in the context of medical discussions about the uvula, it’s essential to treat any term like this with caution – Biyomon Uvula.
When referring to “Biyomon Uvula,” it might imply a uvula condition that could be characterized by significant swelling, elongation, or deviation. Understanding this term in a clinical sense would likely involve recognizing and addressing uvula-related issues that are either exaggerated by fictional concepts or simply rare but treatable medical conditions – Biyomon Uvula.
Possible Uvula Issues in the Context of “Biyomon Uvula”
In the context of this term, patients might be dealing with:
- Severe Uvulitis: Extreme swelling of the uvula (Biyomon Uvula) that mimics the over-exaggeration seen in pop culture references.
- Chronic Uvula Elongation: Uvula growth that reaches an unusual or obstructive length, potentially creating complications with breathing or swallowing.
Since the term “Biyomon Uvula” lacks a basis in formal medical literature, it’s essential to approach any unusual or exaggerated uvula symptoms with medical consultation and evidence-based treatments – Biyomon Uvula.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Uvula-Related Issues
Diagnosis
To diagnose uvula-related issues, a doctor or ENT (ear, nose, and throat) specialist will typically perform a physical examination and may recommend the following:
- Throat Examination: The doctor will visually inspect the throat, uvula, and surrounding tissues for signs of swelling, redness, or elongation.
- Imaging or Endoscopy: In cases of chronic uvula problems, imaging tests or endoscopy may be used to get a clearer view of the upper airway.
- Sleep Study: If sleep apnea or snoring is suspected, the doctor may recommend a sleep study (polysomnography) to assess breathing patterns during sleep.
Treatment Options
Treatment depends on the underlying cause of the uvula condition:
- Medications: Antibiotics, antivirals, antihistamines, and corticosteroids may be prescribed to address infections, allergies, or inflammation.
- Surgical Procedures: Uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP) or laser uvulopalatoplasty (LAUP) are common surgeries to remove or reshape the uvula and soft palate to treat chronic snoring or sleep apnea.
- Lifestyle Modifications: Smoking cessation, hydration, and addressing irritants like acid reflux can help prevent uvula issues.
Preventing Uvula-Related Issues
Although some uvula conditions are unavoidable due to genetic factors or infections, there are several steps you can take to reduce the likelihood of developing uvula-related problems:
- Stay Hydrated: Drinking plenty of water helps keep the uvula and surrounding tissues moist, reducing the risk of swelling due to dehydration.
- Quit Smoking: Smoking irritates the uvula and can cause it to become elongated or swollen over time. Quitting smoking reduces this risk.
- Manage Allergies and Infections: Properly managing allergies and treating infections early can prevent uvulitis and swelling.
- Maintain a Healthy Sleep Environment: If you snore or have sleep apnea, seek medical advice to manage your condition and prevent uvula-related complications.
FAQs
1. What causes uvula swelling and how can I reduce it?
Uvula swelling, or uvulitis, is commonly caused by infections, allergies, dehydration, or trauma. To reduce swelling, stay hydrated, treat the underlying cause (such as an infection or allergy), and use throat sprays or pain relievers for discomfort.
2. Can a swollen uvula cause breathing problems?
In severe cases of uvulitis or uvular swelling, the uvula can become large enough to obstruct the airway, leading to breathing difficulties. If you experience difficulty breathing, seek medical attention immediately.
3. Is an elongated uvula dangerous?
An elongated uvula is not inherently dangerous, but it can cause discomfort, snoring, and difficulty swallowing. In some cases, it may contribute to obstructive sleep apnea, a condition that affects breathing during sleep.
4. Can the uvula be removed?
Yes, the uvula can be removed through a procedure called uvulopalatopharyngoplasty (UPPP). This is usually done to treat chronic snoring or sleep apnea. The procedure removes part of the uvula and soft palate to widen the airway.
5. How do I know if I have a deviated uvula?
A deviated uvula is visible during a throat examination and is typically diagnosed by a healthcare provider. If you notice your uvula leaning to one side or experience related symptoms like snoring or difficulty swallowing, consult a doctor for evaluation.
6. What is the best way to prevent uvula-related problems?
To prevent uvula-related issues, stay hydrated, avoid smoking, treat any infections or allergies promptly, and maintain a healthy sleep environment. Managing underlying conditions like sleep apnea or acid reflux can also help prevent uvula problems.