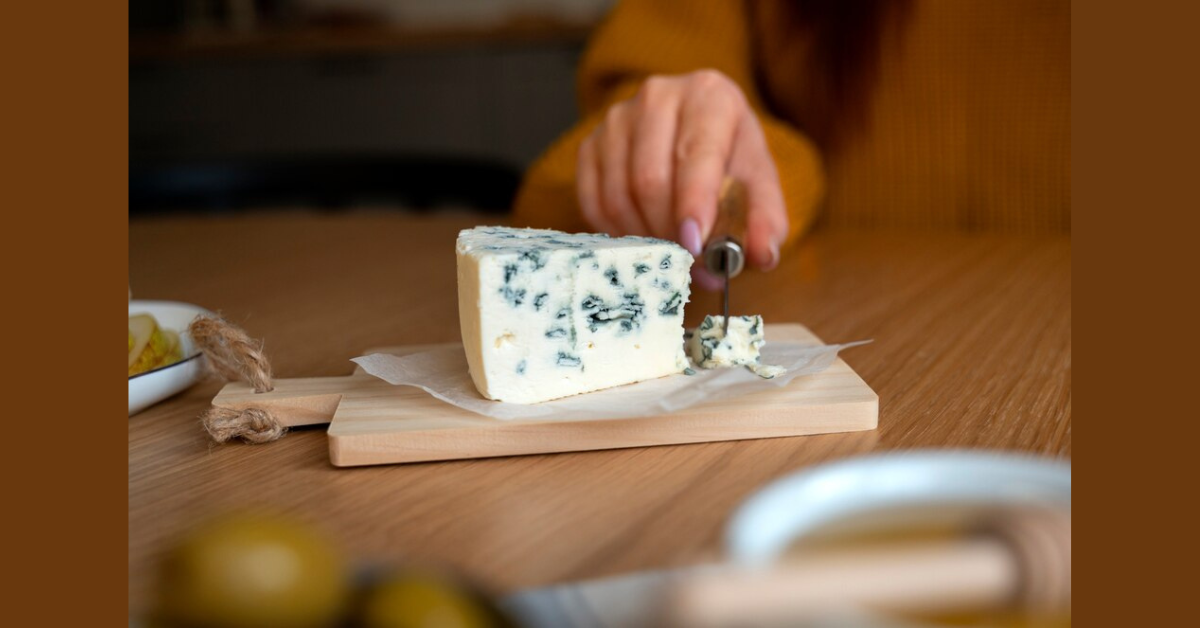
Cheese enthusiasts know that each cheese has its own unique story, flavor profile, and culinary uses. Among these, Gorgonzola stands out for its rich history and distinctive taste. Whether you’re a seasoned cheese aficionado or just starting your cheese exploration, understanding Gorgonzola can elevate your palate and culinary skills. This blog post will guide you through the fascinating world of Gorgonzola’s, revealing its origins, types, health benefits, and versatile uses.
The Origins of Gorgonzola
A Cheese with History
Gorgonzola is one of the oldest blue-veined cheeses, tracing its roots back to Italy over a thousand years ago. It originated in the town of Gorgonzola’s, near Milan, where it was first crafted in the 11th century. The unique climate and the skill of local cheesemakers contributed to the development of Gorgonzola’s distinctive characteristics.
The Making of Gorgonzola
The process of making Gorgonzola involves adding Penicillium glaucum mold to cow’s milk. This mold creates the blue veins that are characteristic of the cheese. The curd is aged for a few months in a cool, damp environment, during which the mold spreads and develops the cheese’s flavor and texture.
Protected Designation of Origin (PDO)
Gorgonzola is a Protected Designation of Origin (PDO) product, meaning it can only be produced in specific regions of Italy under strict guidelines. This designation ensures that the cheese maintains its high quality and traditional production methods.
Types of Gorgonzola
Gorgonzola Dolce
Gorgonzola’s Dolce, also known as “sweet Gorgonzola,” is milder and creamier than its counterpart. It is aged for a shorter period, typically around two months, resulting in a softer texture and a sweeter, more delicate flavor.
Gorgonzola Piccante
Gorgonzola’s Piccante, or “spicy Gorgonzola,” is aged for a longer period, usually three to four months. This extended aging process gives the cheese a firmer texture and a more robust, tangy flavor. It’s perfect for those who enjoy a stronger taste.
Choosing the Right Type
The choice between Gorgonzola’s Dolce and Gorgonzola Piccante depends on your personal preference and intended use. Dolce is ideal for spreading on bread or crackers, while Piccante works well in recipes that call for a bold flavor.
Health Benefits of Gorgonzola
Nutritional Profile
Gorgonzola is rich in essential nutrients, including protein, calcium, and vitamins A and B12. These nutrients support bone health, muscle function, and overall well-being. Despite its creamy texture, Gorgonzola’s contains a moderate amount of fat.
Probiotic Properties
The Penicillium mold used in Gorgonzola production provides probiotic benefits. Probiotics are beneficial bacteria that support a healthy digestive system. Consuming Gorgonzola’s can contribute to gut health and improve digestion.
Potential Health Risks
While Gorgonzola offers many health benefits, it’s important to consume it in moderation due to its high sodium content. People with lactose intolerance or dairy allergies should also be cautious.
Culinary Uses of Gorgonzola
Pairing with Food
Gorgonzola pairs excellently with a variety of foods. Its creamy texture and bold flavor complement fruits like pears, apples, and figs. It also pairs well with nuts, honey, and balsamic vinegar.
Cooking with Gorgonzola
Gorgonzola’s can be used in a wide range of recipes, from salads and pasta dishes to sauces and pizzas. Its melting properties make it an excellent addition to creamy sauces and risottos.
Serving Suggestions
For a simple yet delicious appetizer, spread Gorgonzola’s Dolce on a slice of crusty bread and drizzle with honey. For a more complex dish, try incorporating Gorgonzola’s Piccante into a steak sauce or a stuffed chicken breast recipe.
Storing and Handling Gorgonzola
Proper Storage
To maintain its flavor and texture, Gorgonzola should be stored in the refrigerator, wrapped in wax paper or aluminum foil. This allows the cheese to breathe while preventing it from drying out.
Shelf Life
Gorgonzola’s has a relatively long shelf life compared to other cheeses. When stored properly, it can last up to a month. However, it’s best consumed within two weeks of purchase for optimal flavor.
Serving Tips
Before serving, allow Gorgonzola’s to come to room temperature. This enhances its flavor and makes it easier to spread. Always use a clean knife to prevent cross-contamination with other foods.
Gorgonzola Around the World
Italian Tradition
In Italy, Gorgonzola’s is often enjoyed simply, with a piece of bread and a glass of wine. It’s also used in traditional dishes like Gorgonzola’s gnocchi and polenta.
Global Popularity
Gorgonzola’s unique flavor has made it popular worldwide. It’s found in grocery stores and specialty shops across the globe and is a favorite ingredient in international cuisine.
Culinary Innovations
Chefs around the world are constantly finding new ways to incorporate Gorgonzola’s into their dishes. From gourmet burgers to innovative desserts, Gorgonzola’s versatility continues to inspire culinary creativity.
Conclusion
Gorgonzola is a cheese with a rich history, a variety of types, and numerous health benefits. Its versatile nature makes it a valuable addition to any kitchen, whether you’re a casual cook or a professional chef. By understanding its origins, types, and uses, you can fully appreciate the unique qualities of Gorgonzola and incorporate it into your culinary repertoire.
If you’re ready to explore the world of Gorgonzola’s further, consider booking a tasting session or visiting a specialty cheese shop. And don’t forget to share your Gorgonzola’s creations with our community of cheese lovers!
Enjoy your culinary adventures with Gorgonzola’s—a cheese that truly has something for everyone.
Also Read: Käntäj: Rise of Translation Tools in the Digital Era