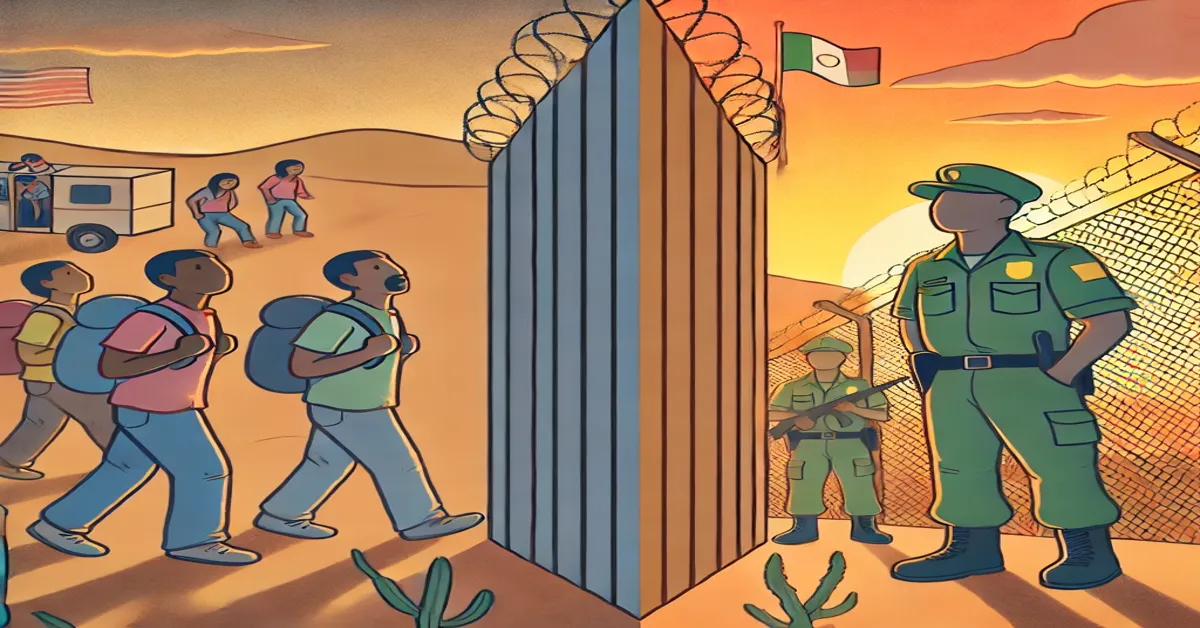
The term “border hopper” is commonly used, often pejoratively, to describe individuals who cross national borders without the proper legal authorization. This practice is a hot-button issue, particularly in regions where migration rates are high, and it is often associated with political, economic, and social debates. However, the term “border hopper” doesn’t fully capture the complex factors that drive people to migrate illegally.
From escaping violence and poverty to seeking better economic opportunities, the motivations behind border hopping are diverse. This article will explore the reasons behind unauthorized border crossings, the challenges that countries face in managing migration, the potential impact on economies, societies, and politics, and the human dimension of migration. Furthermore, we’ll delve into various perspectives on how to approach this multifaceted issue, from border security to humanitarian solutions.
1. Understanding the Meaning of “Border Hopper”
1.1 Definition
A “border hopper” refers to an individual who illegally crosses the borders of a country, typically in an attempt to enter that country without proper documentation. The term can be used to describe various forms of unauthorized entry, including those by foot, vehicle, or other means.
1.2 Origins of the Term
The phrase “border hopper” has its roots in immigration discussions, particularly in regions like the U.S.-Mexico border, where illegal migration has been a long-standing issue. Over time, the term has been applied to individuals who cross into any country illegally. However, it is often used in a derogatory manner, which can dehumanize the people involved in migration.
1.3 Who is Considered a “Border Hopper”?
Those labeled as “border hoppers” are usually individuals trying to flee unsafe or unsustainable living conditions, such as violence, poverty, or political oppression. They may also be people in search of better employment opportunities or access to healthcare and education that are unavailable in their home countries. However, this simplistic term fails to account for the complexity of their experiences and their motivations for risking such a dangerous journey – border hopper.
2. Reasons Behind Unauthorized Border Crossings
2.1 Economic Factors
For many individuals, economic hardship is the main motivator for crossing borders illegally. In countries with high unemployment rates and limited access to resources, people often seek better job opportunities abroad. Some are drawn by the possibility of sending remittances back to their families, which can be a significant source of income for communities in impoverished regions.
2.2 Escaping Violence and Persecution
Many individuals crossing borders illegally are fleeing violent situations, including war, gang violence, and persecution based on religion, ethnicity, or political affiliation. In Central America (border hopper), for example, gang violence and political instability have driven many individuals to seek safety by crossing into countries like the United States, even without proper documentation.
2.3 Environmental and Climate-Related Factors
Another growing reason behind unauthorized migration is environmental and climate-related displacement. Natural disasters, droughts, floods, and rising sea levels are increasingly forcing people to move from their homes, particularly in vulnerable regions. Many people from countries with high exposure to climate-related risks are finding it harder to stay in their homes and are seeking refuge across borders.
2.4 Family Reunification
Family reunification is another reason people may cross borders without the necessary legal documentation. In many cases, family members who have already migrated legally or illegally (border hopper) may wish to bring their relatives to join them, but strict immigration laws make it difficult for families to be reunited through official channels.
3. The Challenges of Managing Border Security
3.1 National Security Concerns
Many countries, particularly those with long land borders, face challenges in maintaining national security while dealing with unauthorized border crossings. Governments are concerned about potential threats, such as the trafficking of drugs, weapons, and even humans across their borders, which can exacerbate domestic security problems (border hopper).
3.2 Human Trafficking and Smuggling Networks
One of the most troubling aspects of border hopping is the involvement of organized criminal networks in facilitating illegal crossings. Smugglers often exploit vulnerable individuals, charging exorbitant fees and subjecting them to dangerous conditions. Human trafficking is also a major concern, as criminal groups may use unauthorized border crossings to traffic individuals for forced labor or sexual exploitation.
3.3 The Cost of Border Enforcement
Border security is expensive. Governments spend billions of dollars annually on fencing, surveillance technologies, border patrol agents, and detention facilities. Despite these investments, managing illegal immigration remains a major challenge. Border walls and checkpoints can only do so much, as determined individuals and well-organized smuggling networks often find ways around them (border hopper).
3.4 Balancing Security and Human Rights
A significant challenge for countries is balancing border security with the need to respect human rights. Migrants often face harsh treatment, including detention in overcrowded facilities, family separations, and even violence. International organizations like the United Nations have called on countries to ensure that their border policies comply with human rights standards and that migrants are treated humanely – border hopper.
4. Economic Impact of Unauthorized Border Crossings
4.1 Labor Markets
Unauthorized immigration can have both positive and negative effects on labor markets. In some cases, undocumented migrants take low-wage jobs that native-born workers are unwilling to accept. This can fill labor shortages in industries like agriculture, construction, and hospitality. However, critics argue that the influx of undocumented workers can drive down wages and lead to job competition for low-skilled native-born workers – border hopper.
4.2 Fiscal Impacts
The fiscal impact of unauthorized immigration is a topic of ongoing debate. Some studies suggest that undocumented migrants contribute more in taxes than they receive in public services, as they often pay sales and property taxes but are not eligible for many government benefits. On the other hand, opponents of illegal immigration argue that undocumented migrants strain public resources, such as healthcare, education, and social services.
4.3 Remittances
One of the significant economic effects of illegal migration is the role of remittances. Migrants who work abroad often send money back to their home countries, providing vital financial support for their families. In many developing countries, remittances account for a significant portion of the national GDP, helping to improve living standards and reduce poverty.
4.4 The Cost of Detention and Deportation
Countries that manage unauthorized immigration must also contend with the costs associated with detention and deportation. Detaining migrants can be expensive, as it involves providing housing, food, and medical care for individuals awaiting legal proceedings. Deporting individuals is also costly, as it involves legal processes, transportation, and coordination with foreign governments – border hopper.
5. The Social and Cultural Impact of Unauthorized Immigration
5.1 Integration Challenges
One of the biggest challenges unauthorized immigrants face is integrating into their new communities. Language barriers, cultural differences, and legal status can make it difficult for these individuals to access education, healthcare, and job opportunities. Many undocumented immigrants live in fear of deportation, which can lead to social isolation and marginalization – border hopper.
5.2 Cultural Contributions
Despite the challenges they face, undocumented immigrants often make significant cultural contributions to the societies they join. Many bring unique traditions, cuisines, and art forms that enrich the cultural fabric of their new homes. In regions with high levels of immigration, these cultural contributions can lead to greater diversity and a more vibrant community life.
5.3 The Impact on Native Populations
Unauthorized immigration can also have an impact on native populations, particularly in regions with high levels of migration. Some individuals may feel threatened by the arrival of new immigrants, leading to tensions over issues like job competition, access to public services, and cultural differences. However, others may welcome the diversity and the contributions that immigrants bring to their communities – border hopper.
6. Legal and Political Responses to Border Hopping
6.1 Immigration Laws and Policies
Countries have responded to the issue of illegal immigration with a variety of legal and policy measures. In some cases, governments have tightened immigration laws, increased border security, and expanded detention and deportation programs. In other instances, countries have sought to address the root causes of migration, such as poverty and violence, through foreign aid and development programs – border hopper.
6.2 Border Walls and Physical Barriers
One of the most visible responses to unauthorized border crossings has been the construction of physical barriers, such as border walls and fences. While these structures can deter some migrants, they are not foolproof. Determined individuals and smuggling networks often find ways to bypass these barriers, whether by digging tunnels, using ladders, or crossing through remote areas.
6.3 International Cooperation and Migration Agreements
Addressing the issue of illegal immigration often requires international cooperation. Countries that are major sources of migration may enter into agreements with destination countries to improve border security, combat human trafficking, and promote legal pathways for migration. Additionally, international organizations like the United Nations play a role in advocating for the rights of migrants and providing humanitarian assistance to those in need – border hopper.
7. Humanitarian Concerns and Migrant Rights
7.1 The Human Cost of Border Hopping
For many migrants, crossing a border without proper documentation is a dangerous and traumatic experience. Migrants may face physical violence, exploitation by smugglers, and the risk of death while attempting to cross remote deserts, rivers, or seas. Once they arrive in their destination country, they may be subject to detention, family separation, and deportation.
7.2 Migrant Advocacy and Support Organizations
Numerous organizations around the world work to support undocumented migrants and advocate for their rights. These groups provide legal assistance, shelter, medical care, and other forms of support to migrants in need. They also work to raise awareness about the challenges that undocumented immigrants face and advocate for policy changes to protect their rights.
7.3 The Debate Over Amnesty and Pathways to Legalization
One of the most contentious debates in immigration policy is whether countries should offer amnesty or pathways to legalization for undocumented immigrants. Proponents argue that providing legal status to long-term undocumented residents can help them integrate into society, contribute to the economy, and reduce the strain on immigration enforcement systems. Opponents, however, argue that offering amnesty encourages further illegal immigration and undermines the rule of law.
Conclusion
The issue of border hopping is complex and multifaceted, involving a range of economic, social, and political factors. While unauthorized immigration presents significant challenges for both migrants and destination countries, it is important to recognize the human dimension of this issue. Migrants are often driven by a desire for safety, security, and opportunity, and addressing the root causes of migration is essential for finding long-term solutions.
As countries grapple with the challenges of managing border security and addressing the needs of migrants, it is crucial to strike a balance between enforcing immigration laws and protecting human rights. By fostering international cooperation, promoting legal pathways for migration, and addressing the underlying factors that drive migration, countries can work toward a more just and humane approach to immigration.
FAQs
1. What does the term “border hopper” mean? The term “border hopper” refers to an individual who crosses national borders without legal authorization. It is often used to describe illegal immigration, but it can carry negative connotations.
2. Why do people engage in unauthorized border crossings? People cross borders illegally for various reasons, including escaping violence, poverty, or persecution, seeking better economic opportunities, and reuniting with family members.
3. What are the economic impacts of unauthorized immigration? Unauthorized immigration can have both positive and negative effects on the economy. While undocumented migrants may fill labor shortages and contribute to the economy through taxes, critics argue that they can strain public resources like healthcare and education.
4. How do countries address unauthorized immigration? Countries use a variety of methods to address illegal immigration, including border walls, enhanced security measures, detention, deportation, and international agreements aimed at curbing migration.
5. What are the humanitarian concerns surrounding illegal border crossings? Migrants who cross borders illegally often face dangerous conditions, exploitation by smugglers, and the risk of detention and deportation. Human rights organizations advocate for the humane treatment of migrants and the protection of their rights.
6. Is there a solution to unauthorized border crossings? There is no one-size-fits-all solution to unauthorized immigration. Addressing the root causes of migration, such as poverty and violence, promoting legal pathways for migration, and fostering international cooperation are all important steps toward finding long-term solutions.
4o